Used to quickly create preliminary building designs and
executing energy calculations and simulations to analyze the proposed
building's energy performance. Conceptual Design creates a simple
OpenBuildings Energy Simulator project; a building with
floors, rooms, glazing, thermal zones and HVAC systems, and provides the
ability to change aspects of concept building to simulate varying design
scenarios.
Opens when creating new
OpenBuildings Energy Simulator projects or opening DGN files
that are not valid
OpenBuildings Energy Simulator files and selecting the
Conceptual Project option provided on the
Create Energy Services Project dialog (see .
Create a New Conceptual
Design)
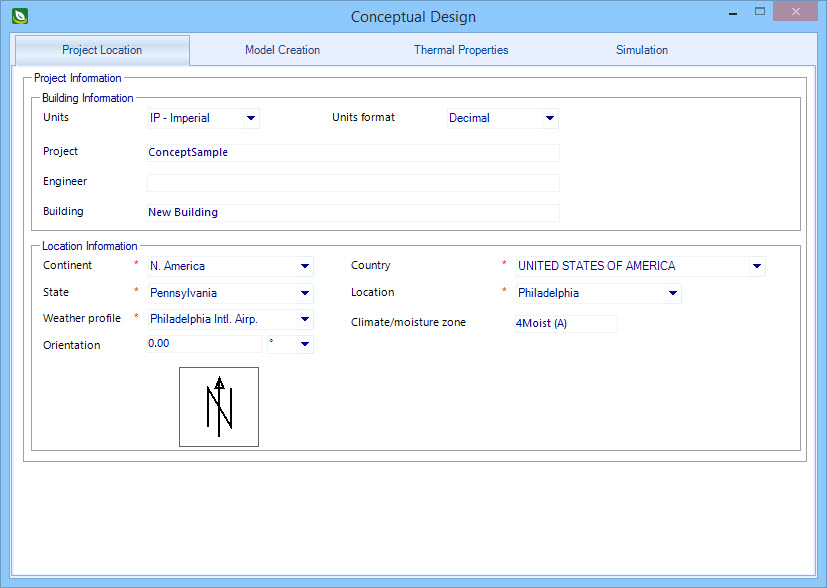
Project Location
tab
The
Conceptual Design dialog opens to the Project
Location tab by default. Here you enter basic project information for the
building and the building location.
| Setting | Description |
|---|
| Building Information
|
Contains settings used to enter basic information
about the proposed building including units and unit format.
- Units - Used to
select between IP-Imperial and SI-Metric units systems for the project. The
units system selected here persists throughout the user interface where units
are displayed.
- Units
Format - Used to set the units format using the IP-Imperial units
system. The options allow you to display values using either decimal or
fraction formats. Units Format is disabled when the project units are set to SI
- Metric.
- Project - Used
to enter a name for the project.
- Engineer - Used
to enter a name for the engineer who is in charge of the project.
- Building - Used
to enter a name for the proposed building.
|
| Location Information
|
Contain settings used to define the proposed building
location and select the weather profile nearest to the building location as
well as the building orientation and the climate and moisture zone
classification.
- Continent -
Used to select the continent in which the proposed building site is located. By
default, the continent property is determined by the settings in the Defaults
Manager dialog box. Use the drop-down list to select the continent applicable
to your project site. The continent selection made here filters the Country
drop-down list to display only the countries located on the selected continent.
- Country - Used
to select the country your proposed building site is located. The selection
made here filters the State/Province drop-down list to display only the states
or provinces located in the selected country.
- State - Used to
select the state or province your proposed building site is located. The
selection made here filters the Location drop-down list to display only the
weather locations found in the selected state or province.
- Location - Used
to select the nearest weather station to your project site.
- Weather
profile - Used to select from a list of
weather data profiles
that are located near the conceptual building
site.
- Climate/Moisture
Zone - Used to set the climate and moisture zones in which the
project site is located. Climate zones are specified with a number (1 through
8) and moisture zones, a letter (A, B or C).
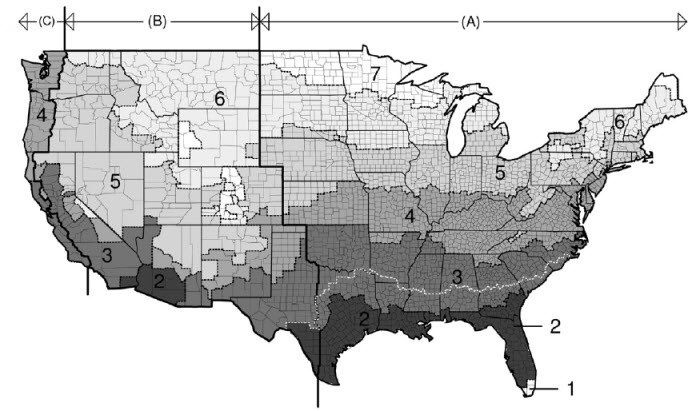
The
2006 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) Climate Zone map of the
continental United States of America
- Orientation -
Used to set the orientation of the building. Orientation refers to solar
orientation which is the siting of the building with respect to solar access.
The orientation value entered here defines the angle between the building
y-axis and true north in the clockwise direction. A rotation of 180 degrees
flips the building around so that the north (or back) facade is facing south
(or front).Orientation has an impact on heating, lighting and cooling costs. By
maximizing southern exposure, the building design can take advantage of the sun
for daylight and passive solar heating. This results in lower cooling costs by
minimizing western exposures, where it's most difficult to provide shade from
the sun.
|


